Cognitive Exam #2 Bingo Cards - Print Free or Customize
Print free Cognitive Exam #2 bingo cards or personalize, unlimited prints! Select from 26,900+ designs or use our bingo card generator. Add numbers, phrases, pictures, or mix them all. Play using PDF printouts, online bingo cards, and our online bingo caller, or go hybrid.
About: This bingo card is perfect for psychology students or anyone interested in the science of learning, memory, and behavior. The prompts are based on key concepts from cognitive and behavioral psychology, engaging players to recall, apply, and discuss real-world examples. It's great for classroom review sessions, study groups, or introductory workshops on how we think, learn, and communicate.
How To: To save a printable PDF, click the Print button. You can modify the card count and other printing preferences on the Print tab. Grid items and free space text can be edited on the Basic tab. Appearance can be completely customized on the relevant tabs, or you can quickly search any preference using the 🔍 tab.
How to play Cognitive Exam #2 Bingo Cards?
- Paper Players: Print PDF bingo cards and physically cross off the cards.
- Digital Players: Click on the Play button above, and then click on the 🎫 button.
- Paper Caller: Print PDF calling list & calling slips and physically draw the slips.
- Digital Caller: Click on the Play button above.
- Mixed Mode: Pick any combination above. For instance, caller can be either Printed or Digital. And players can be Printed or Digital or a combo of both.
Step-By-Step:
- Start by saving the Cognitive Exam #2 PDF by clicking on the "Print" button above.
- Open the PDF and print it.
- For random calling, you can print another copy of the call list, cut, fold and then pull them randomly at play time.
- Cut the bingo cards at the cut marks if there are greater than 1 bingo cards per page.
- Give one card to each player. For marking, you can use pens. Crayons are the cheapest.
- Pick one person to be the caller. If you are playing in a small group, the caller may also play along with their own Bingo card.
- The caller begins the game by randomly pulling an item from the call list and calling out it to all players.
- The players scan their cards to see if they have the called word. If they do, they mark that word.
- The first player to finish a horizontal, vertical, or a diagonal line of crossed items shouts "Bingo!" and wins the game.
- The caller verifies that the items marked form a correct line as per the Bingo card and call list.
- You can play for different patterns or a full card blackout for a longer game.
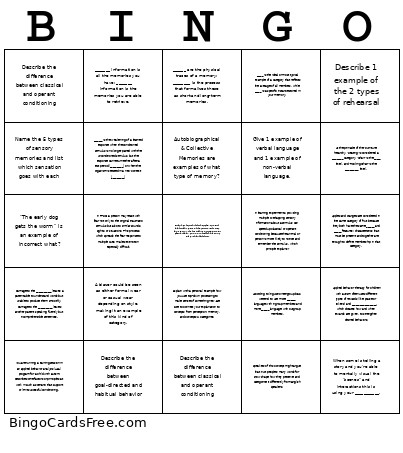 This Cognitive Exam #2 Bingo Cards Game contains following Words or Phrases: Name the 5 types of sensory memories and list which sensation goes with each, "The early dog gets the worm" is an example of incorrect what?, Apples and oranges are considered in the same category of fruit because they both have the same ______ and ______ features: characteristics that must be present and together are enough to define membership in that category., Describe the difference between classical and operant conditioning, Describe the difference between classical and operant conditioning, Autobiographical & Collective Memories are examples of what type of memory?, Give 1 example of verbal language and 1 example of non-verbal language., _____ is the ideal or most typical example of a category that reflects the average of all members, while _____ is a specific instance stored in your memory., Applied behavior therapy for children with autism often uses different types of rewards (like praise or tokens) and ___________________, which dictates how and when rewards are given, to strengthen desired behaviors., Damage to the ____________ leaves a patient able to understand words but unable to produce them smoothly. Damage to the ___________ leaves another patient speaking fluently but incomprehensible sentences., ______ are the physical traces of a memory; ________ is the process that formalizes these as short and long-term memories., When some is telling a story and you're able to mentally visual the "scenes" and interactions this is using your ___________., At the pinnacle of the 'Furniture' hierarchy, 'Seating' is considered a _________ category, 'Chair' is the _____ level, and 'Rocking Chair' is the ___________ level., Describe the difference between goal-directed and habitual behavior, In learning experiments, providing multiple overlapping sensory information about a stimulus can speed up classical or operant conditioning because the animal or person is more likely to notice and remember the stimulus. Which principle explains?, _______ information is all the memories you have; _______ information is the memories you are able to retrieve., Speakers of this concept might argue that Inuit people's many words for snow shape how they perceive and categorize it differently from English speakers., A blazer could be seen as either formal wear or casual wear depending on style, making it an example of this kind of category., _______ is the weakening of a learned response when the conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with the unconditioned stimulus, but the response can return either after a rest period (__________) or when the organism is tested in a new context (__________), Explain with a personal example how you use top-down processing to make sense of something new. Be sure to connect your explanation to concepts from perception, memory, and concepts & categories., Describe 1 example of the 2 types of rehearsal, According to linguistic intergroup bias, we tend to use more _______ language with ingroup members and more ______ language with outgroup members., Choose an example of a borderline member of a category that might be perceived differently across cultures (e.g., a food, clothing item, or social behavior). Explain why people from different cultural backgrounds might categorize it differently, and how prior knowledge, experience, or cultural schemas influence these perceptions., In PTSD, a person may react with fear not only to the original traumatic stimulus but also to similar sounds, sights, or situations. This process, which spreads the fear response to multiple cues, makes extinction especially difficult., You are running a training session in an applied behavior analysis (ABA) program for a child with autism. Describe some factors or principles at work in such a scenario that support or limit successful conditioning..
This Cognitive Exam #2 Bingo Cards Game contains following Words or Phrases: Name the 5 types of sensory memories and list which sensation goes with each, "The early dog gets the worm" is an example of incorrect what?, Apples and oranges are considered in the same category of fruit because they both have the same ______ and ______ features: characteristics that must be present and together are enough to define membership in that category., Describe the difference between classical and operant conditioning, Describe the difference between classical and operant conditioning, Autobiographical & Collective Memories are examples of what type of memory?, Give 1 example of verbal language and 1 example of non-verbal language., _____ is the ideal or most typical example of a category that reflects the average of all members, while _____ is a specific instance stored in your memory., Applied behavior therapy for children with autism often uses different types of rewards (like praise or tokens) and ___________________, which dictates how and when rewards are given, to strengthen desired behaviors., Damage to the ____________ leaves a patient able to understand words but unable to produce them smoothly. Damage to the ___________ leaves another patient speaking fluently but incomprehensible sentences., ______ are the physical traces of a memory; ________ is the process that formalizes these as short and long-term memories., When some is telling a story and you're able to mentally visual the "scenes" and interactions this is using your ___________., At the pinnacle of the 'Furniture' hierarchy, 'Seating' is considered a _________ category, 'Chair' is the _____ level, and 'Rocking Chair' is the ___________ level., Describe the difference between goal-directed and habitual behavior, In learning experiments, providing multiple overlapping sensory information about a stimulus can speed up classical or operant conditioning because the animal or person is more likely to notice and remember the stimulus. Which principle explains?, _______ information is all the memories you have; _______ information is the memories you are able to retrieve., Speakers of this concept might argue that Inuit people's many words for snow shape how they perceive and categorize it differently from English speakers., A blazer could be seen as either formal wear or casual wear depending on style, making it an example of this kind of category., _______ is the weakening of a learned response when the conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with the unconditioned stimulus, but the response can return either after a rest period (__________) or when the organism is tested in a new context (__________), Explain with a personal example how you use top-down processing to make sense of something new. Be sure to connect your explanation to concepts from perception, memory, and concepts & categories., Describe 1 example of the 2 types of rehearsal, According to linguistic intergroup bias, we tend to use more _______ language with ingroup members and more ______ language with outgroup members., Choose an example of a borderline member of a category that might be perceived differently across cultures (e.g., a food, clothing item, or social behavior). Explain why people from different cultural backgrounds might categorize it differently, and how prior knowledge, experience, or cultural schemas influence these perceptions., In PTSD, a person may react with fear not only to the original traumatic stimulus but also to similar sounds, sights, or situations. This process, which spreads the fear response to multiple cues, makes extinction especially difficult., You are running a training session in an applied behavior analysis (ABA) program for a child with autism. Describe some factors or principles at work in such a scenario that support or limit successful conditioning..